Nail Fungus Can Be Painful
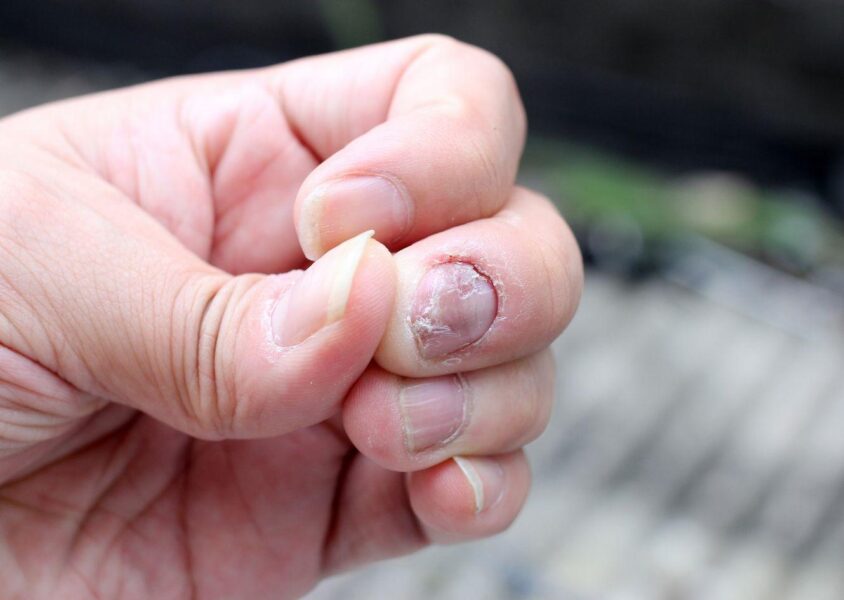
Nail fungus, also known as onychomycosis or tinea unguium, is a common condition affecting the fingernails or toes. It is caused by a fungus called a dermatophyte, which feeds on keratin, the protein that makes up the nails. Other types of fungi, as well as yeast and mold, can also cause nail fungus.
Older adults are more likely to develop fungus as the nails become thicker and more brittle with age, making them more prone to infection. In addition, failing to keep the nails clean and trimmed can increase the risk of fungus on your nails.
Nails that are damaged or injured are more susceptible to infection. In addition, wearing shoes that are too tight can create a warm and moist environment for fungi to thrive. And excessive sweating can create a moist environment that is conducive to the growth of fungi.
Certain medical conditions, such as diabetes, circulatory problems, and a weakened immune system, can increase the risk of nail fungus. In addition, spending a lot of time in pools or other bodies of water can increase the risk of fungus, as the fungi that cause the infection can survive in water. Using nail clippers, files, or other personal grooming items used by someone with nail fungus can also increase the risk of infection.
The symptoms of nail fungus are hard to ignore. The nails may become thick and difficult to trim. They may become brittle and break easily. Sometimes, the nails become yellow, brown, or green and may produce a foul smell. It may lift off the nail bed, causing pain and discomfort. Sometimes, white spots may also appear on the nails.
Treating Nail Fungus
Antifungal medication is the most common treatment for fungus. In addition, your healthcare provider may prescribe an oral antifungal medication. Such medications include terbinafine (Lamisil) or itraconazole (Sporanox), or topical medication, such as efinaconazole (Jublia) or amorolfine (Loceryl). These medications work by killing the fungi that cause the infection.
Only your medical practitioner can prescribe topical ointments, such as miconazole (Monistat) or clotrimazole (Lotrimin). You would apply these ointments directly to the affected nail.
Laser treatment can be an effective option for treating fungus. They may use a laser to kill the fungi that cause the infection. In severe cases of fungus, your healthcare provider may recommend surgically removing the infected nail.
No one would recommend to ignore nail fungus. If left untreated, fungus can cause the infected nail to become thicker, harder, and more brittle, and it may become painful to wear shoes or walk. The infection can also spread to other nails, leading to more serious health problems.
In addition, ignoring nail fungus can lead to a delay in treatment, making it more difficult to clear the infection. If you suspect nail fungus, it is important to see a healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis and treatment. Early treatment can help prevent the infection from worsening and can help improve the chances of a successful outcome. It is also important to follow the treatment plan recommended by a healthcare provider. And complete the entire treatment course to ensure the infection is completely cleared.