Insulin Is A Life Saver for Diabetic Patients
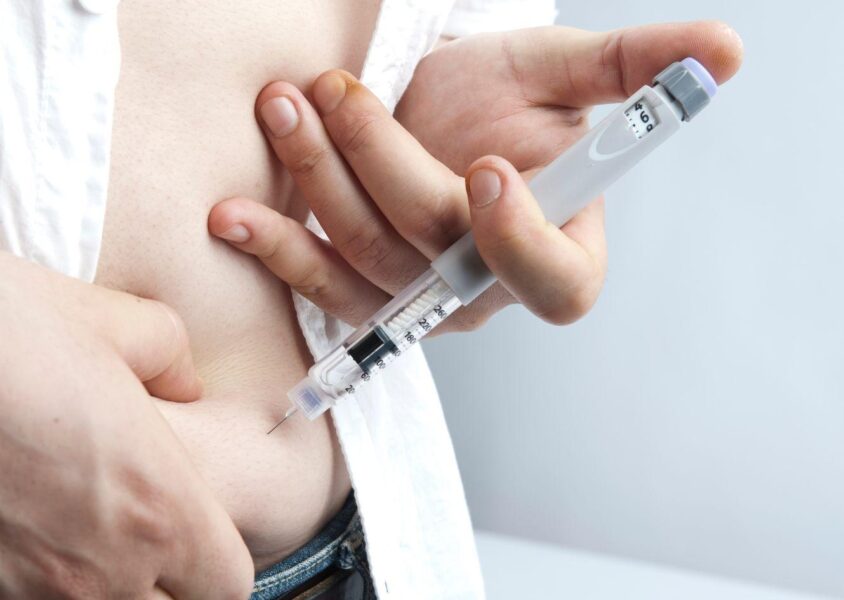
Insulin is a hormone that the pancreas produces. It helps regulate blood sugar levels in the body. However, in people with diabetes, the body either does not produce enough insulin. Or, it does not properly use that it does produce. As a result, it leads to high blood sugar levels, which can cause various health problems.
Insulin helps lower blood sugar levels by allowing glucose to enter cells, which can be used for energy. When you eat food, your body breaks down the carbohydrates into glucose, which then enters your bloodstream. It acts as a key, allowing glucose to enter cells and be used for energy.
Several types of insulin are available, including rapid-acting, short-acting, intermediate-acting, and long-acting. The type and dose will depend on their specific needs and the type of diabetes.
In people with type 1 diabetes, the body does not produce any insulin. So, they must take its injections or use an pump to get the amount they need. In people with type 2 diabetes, the body may not produce enough of it or may not use it effectively. So they may need to take its injections or oral medications to help lower blood sugar levels.
Insulin Types And Schedules
Insulin can help prevent or reduce the risk of complications associated with diabetes. Complications include heart disease, kidney damage, nerve damage, and eye problems. Therefore, people with diabetes need to work with their healthcare team to determine the best treatment plan.
The frequency and timing of injections or insulin pump therapy will depend on the type one uses and the specific needs of the individual.
In general, one would usually take rapid-acting and short-acting insulins before or with meals. This is to help control blood sugar levels after eating.
One would take Intermediate-acting insulin once or twice a day to provide a longer-lasting effect. Finally, long-acting insulin is once or twice a day to provide a consistent background level.
The specific insulin regimen for an individual with diabetes will depend on several factors. These factors include age, weight, type of diabetes, diet, and physical activity level. Therefore, people with diabetes need to work closely with their healthcare team to determine the best regimen.
In addition to injections or pump therapy, people with diabetes may also need to monitor their blood sugar levels regularly and adjust their doses or other aspects of their treatment plan. That can help ensure that blood sugar levels well-controlled and help prevent or reduce the risk of complications associated with diabetes.
Insulin is an important treatment for diabetes, but it is not a cure. Diabetes is a chronic condition that occurs when the body is unable to properly regulate blood sugar levels, either because it does not produce enough insulin or because it does not use it effectively.